Home
Home | About Us | Advantages | Blogs | Contact Us
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Home | About Us | Advantages | Blogs | Contact Us
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-03-28 Origin: Site








Sanitary Napkin Materials Guide
Comprehensive guide to materials used in modern sanitary napkins - structure, composition, and selection criteria
Sanitary napkins are made of three main components:
Non-woven fabrics (thermal bonding, spunlace, spunbond)
Cotton material
Perforated PE film
Bamboo fiber
Fluff pulp
Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP)
Airlaid paper
ADL (Acquisition Distribution Layer)
Polyethylene film (PE film)
Breathable PE film
Non-woven fabric composites
Additional materials: Hot melt adhesive, release paper, easy tape, leak guards, and functional chips.
The global sanitary napkin market is witnessing substantial growth. According to IMARC Group research, the market size was valued at USD 28.0 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 38.0 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.46% from 2025 to 2033 (IMARC Group, 2025). Disposable sanitary napkins have become nearly a public necessity for women, yet despite their widespread use and frequent discussions in public forums, there remains a significant gap in consumer knowledge regarding their composition.
"If you were to interview ten women around you, at most, only one might vaguely explain the materials used to make sanitary napkins."
In a consumer-driven society, our understanding of products often stops at the level of user experience. We tend to explore the "why" and "how" of a product only when we particularly like or need it. This lack of detailed knowledge about sanitary napkins is quite common. Given the importance of these products in daily life, it is essential to delve deeper into their structure and materials to better understand their functionality and impact on health and the environment.
Sanitary napkins generally consist of three main components:
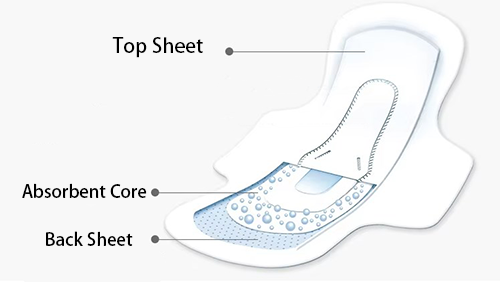
The top sheet is the part of the sanitary napkin that directly contacts the skin. Its primary functions are to absorb liquid and quickly guide it into the absorbent core.
Quick Absorption: The top sheet material must rapidly absorb liquid to prevent it from lingering on the surface, thereby keeping the skin dry.
Comfort: The material should be soft and skin-friendly, reducing friction and irritation to enhance user comfort.
Breathability: Good breathability reduces the dampness and stuffiness against the skin, lowering the risk of allergies and discomfort.
Guiding Permeation: The top sheet should quickly channel liquid into the absorbent core to prevent backflow and leakage.
The absorbent core is the central part of the sanitary napkin, responsible for absorbing and locking in menstrual blood and other liquids to prevent backflow and leakage, thus maintaining the dryness of the napkin's surface and providing a comfortable user experience.
Quick Absorption: The absorbent core can quickly absorb liquid, reducing the time it stays on the surface of the napkin and keeping it dry.
Preventing Leakage: Through rational structural design and material combination, the absorbent core can effectively prevent liquid from leaking out, offering better protection.
Locking in Liquid: High Absorbency Polymer (SAP) can absorb and lock in liquid, preventing it from flowing back and extending the napkin's usage time.
The back sheet material, also known as the bottom film or back layer, is an essential part of the sanitary napkin. Its main function is to prevent liquid from seeping through, while also offering a certain degree of breathability to enhance user comfort.
Preventing Seepage: The primary function of the back sheet is to prevent menstrual blood and other liquids from seeping through to clothing, ensuring the user remains clean and comfortable during use.
Breathability: Some back sheet materials are breathable, reducing the contact between the skin and non-breathable materials, thereby lowering the risk of skin allergies and discomfort.
Softness: The back sheet material typically needs to have a certain degree of softness to enhance user comfort.
These include hot air through non-woven fabrics and thermal calendaring non-woven fabrics.
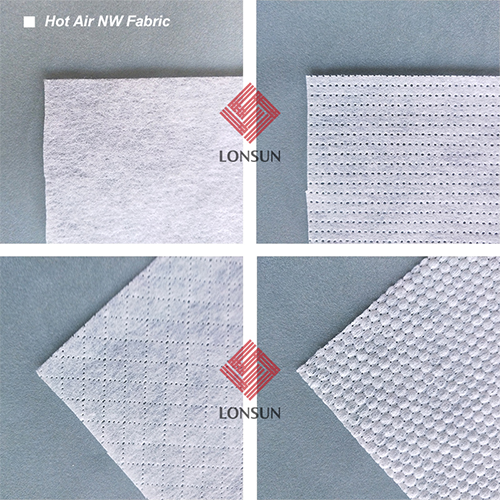
During production, a certain proportion of low-melting-point bonding fibers or bicomponent fibers are usually mixed into the fiber web. After the fibers are combed into a web, hot air from the drying equipment penetrates the web, causing it to bond and form the non-woven fabric. The product features good fluffiness, softness, and excellent permeability.
After the fibers are combed into a web, they are pressed by calendering rollers (under certain high temperature and pressure) to melt the low-melting-point fibers and bond them into a web, resulting in a smooth surface with calendering points. The product is characterized by its lightness and softness.
Generally, only spunlace non-woven fabric made from 100% cotton can be used for the surface of sanitary napkins. It has good wear resistance, is soft and skin-friendly, and has good water absorption (it becomes wet after use).
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is made of polypropylene (PP) and has the characteristics of low density, low hygroscopicity, high strength and high elongation. It is a popular option for the surface layer of sanitary napkins. SSS nonwoven fabric and SMMS nonwoven fabric are popular among manufacturers of disposable sanitary products.
Cannot be used for the surface of sanitary napkins but can be used for the sides (i.e., wings).
Single hydrophilic, multiple hydrophilic.
The hydrophilicity of non-woven fabrics mainly depends on the oil agent on the fiber surface. Oil agents can be classified into single hydrophilic (i.e., single hydrophilic), multiple hydrophilic (i.e., multiple hydrophilic), and weak hydrophilic. Therefore, depending on the type of oil agent used, non-woven fabrics can be divided into single hydrophilic non-woven fabrics, multiple hydrophilic non-woven fabrics, and weak hydrophilic non-woven fabrics.
For the penetration of liquid, the first penetration is relatively fast, and the speed of subsequent liquid penetration gradually slows down.
This is the most commonly used type of material in sanitary products. Its products have good water absorption, and the ability to penetrate liquid multiple times is strong. The penetration time for the second or even third liquid is also short.
This is a relatively new concept that has emerged in the past two years. Its product features good vertical seepage effect, no horizontal diffusion on the surface, diffusion after penetrating to the lower layer (a lower layer material with strong diffusion is needed), low backflow, and a relatively dry surface. After absorbing liquid, the surface appears cleaner due to the smaller contact area.
Characteristics: Cotton material is natural, soft, and skin-friendly, causing no irritation to the skin and is suitable for sensitive skin. It can provide a more comfortable user experience.
Application: It is commonly used in high-end sanitary napkin products, especially those designed for sensitive skin.
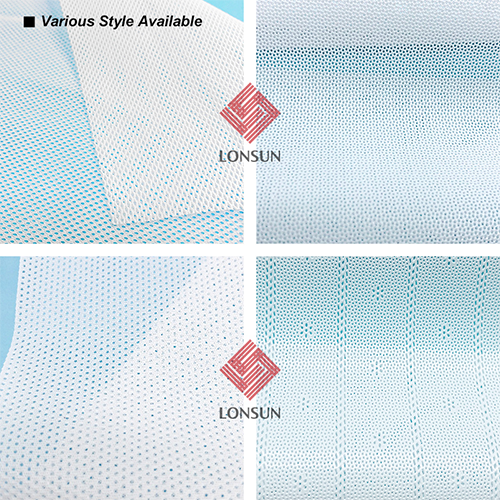

Characteristics: Perforated PE film is a thin plastic film with tiny holes on its surface, which can quickly absorb liquid and keep the surface dry. However, its breathability is relatively poor, which may cause skin discomfort.
Application: It is suitable for sanitary napkin products with high dryness requirements but is not recommended for sensitive skin.
Characteristics: Bamboo fiber has natural antibacterial and breathable properties, is soft and skin-friendly, and can provide good comfort and hygiene performance.
Application: In recent years, bamboo fiber has been increasingly used in high-end sanitary napkin products and is favored by consumers for its eco-friendly and natural characteristics.
Comfort: Cotton and bamboo fiber materials offer higher comfort and are suitable for sensitive skin.
Absorption Performance: Non-woven fabrics and perforated films have better absorption performance and can quickly absorb liquid.
Breathability: Cotton and bamboo fiber materials have better breathability, reducing the dampness and stuffiness against the skin.
Cost: Non-woven fabrics are cost-effective and suitable for mid-to-low-end products, while cotton and bamboo fiber materials are more expensive and suitable for mid-to-high-end products.
Naturalization: With the increasing demand for natural materials from consumers, the application of natural materials such as cotton and bamboo fiber is becoming more widespread.
Multifunctionalization: Top sheet materials are not only required to have good absorption and breathability but may also incorporate functions such as antibacterial and deodorizing properties.
Personalization: Depending on the needs of different users, the performance and functions of top sheet materials may become more diverse and personalized.
The absorbent core is the central part of the sanitary napkin, and its performance directly affects the usage effect and user comfort. By reasonably selecting and combining materials, the performance of the absorbent core can be improved to meet the needs of different users.
Fluff pulp is one of the main components of the absorbent core, usually made from wood pulp. It is a soft fibrous material with good absorption properties, capable of quickly absorbing liquid. The fibrous structure of fluff pulp can increase the fluffiness and absorption speed of the absorbent core.
SAP is a synthetic material with extremely high water absorption capacity, able to absorb several to tens of times its own weight in liquid. SAP particles are usually distributed in the fluff pulp. When liquid is absorbed, SAP swells and locks in the liquid, preventing it from flowing back.
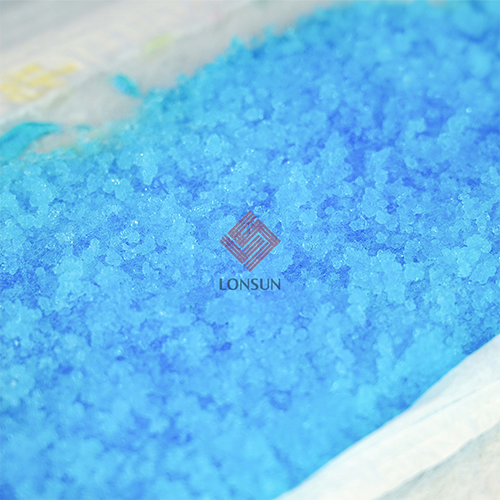
Airlaid paper is a material used to wrap the absorbent core, usually made from wood pulp. It has good breathability and certain absorption properties, preventing the leakage of fluff pulp and SAP particles.

Regular Absorbent Core: Composed of fluff pulp and super absorbent polymer, this is the most common type of absorbent core.
Thickened Absorbent Core: Based on the regular absorbent core, the thickness is increased to enhance absorption capacity, suitable for heavier flow situations.
Ultra-thin Absorbent Core: By optimizing the materials and structural design, the absorbent core is made thinner while maintaining good absorption properties.
Absorption Speed: The speed at which the absorbent core absorbs liquid, usually measured in seconds.
Absorption Capacity: The total amount of liquid the absorbent core can absorb, usually measured in milliliters.
Backflow: The amount of liquid that seeps back to the surface of the sanitary napkin after the absorbent core has absorbed the liquid.
Breathability: The breathability of the absorbent core affects user comfort.
The back sheet material of sanitary napkins, while ensuring liquid impermeability, can significantly enhance user comfort and experience by improving breathability and softness.

Characteristics: Polyethylene film is one of the most common back sheet materials, known for its good waterproof performance, light weight, flexibility, and low cost.
Application: Widely used in mid-to-low-end sanitary napkin products, effectively preventing liquid seepage.
Characteristics: Breathable PE film is usually made from polyethylene or other composite materials. It is waterproof while also offering a certain degree of breathability. This material allows water vapor to pass through while preventing liquid from doing so, thereby reducing the dampness and stuffiness against the skin.
Application: Suitable for mid-to-high-end sanitary napkin products with higher comfort requirements, helping to reduce skin allergies and discomfort.
Characteristics: Non-woven fabric has good breathability and softness, but its waterproof performance is relatively weak. It usually needs to be used in combination with other materials to enhance impermeability.
Application: In some high-end sanitary napkin products, non-woven fabric may be combined with breathable film to balance breathability and impermeability.
Comfort: Breathable film and non-woven fabric have better breathability and are more comfortable for long-term use.
Impermeability: Polyethylene film has the strongest impermeability, suitable for heavier flow situations.
Cost: Polyethylene film is cost-effective and suitable for mid-to-low-end products, while breathable film and non-woven fabric are more expensive and suitable for mid-to-high-end products.
Multifunctionalization: With the advancement of technology, back sheet materials are not only required to have good impermeability and breathability but may also incorporate functions such as antibacterial and deodorizing properties.
Eco-friendliness: The use of eco-friendly materials is increasingly important. Some new types of biodegradable materials are being researched and applied to reduce environmental impact.
Personalization: Depending on the needs of different users, the performance and functions of back sheet materials may become more diverse and personalized.

Hot melt adhesive is primarily used in sanitary napkin manufacturing to bond the top sheet, absorbent core, and back sheet, ensuring that the layers do not separate during use. It is also used to fix additional components such as leak guards.
Hot melt adhesive is a thermoplastic material that melts into a liquid state when heated and solidifies upon cooling to form a bond. It is composed mainly of polymers and some additives (such as tackifiers, waxes, and antioxidants). In the production of sanitary napkins, the hot melt adhesive is melted by heating equipment and evenly applied between different layers of the napkin. After cooling, it forms a strong bond.
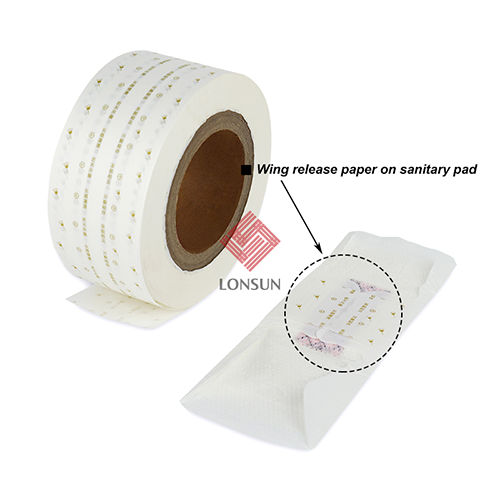

Release paper, also known as release liner or peel paper, is a special material used in sanitary napkins to protect the adhesive on the back.
Protecting Adhesive: Release paper covers the adhesive area of the sanitary napkin, preventing the adhesive from coming into contact with other objects or dust and impurities in the air during storage and transportation, maintaining the cleanliness and tackiness of the adhesive.
Ease of Use: When using the sanitary napkin, users can easily tear off the release paper to expose the adhesive and then attach the napkin to their underwear. The easy-tear property of the release paper ensures convenient use.

Easy tape is a type of environmentally friendly tape that facilitates the re-packaging and disposal of sanitary napkins.
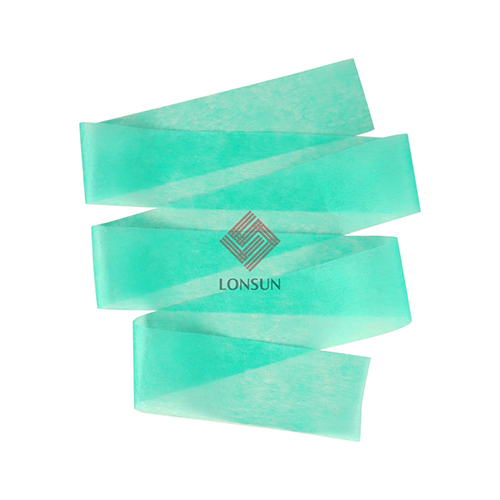
The acquisition distribution layer (ADL) of a sanitary pad is a special material located between the top sheet and the absorbent core.
Quick downward seepage: The ADL can quickly conduct liquid from the surface layer to the absorbent core, reducing the dwell time of liquid on the surface layer.
Horizontal diffusion: It can conduct liquid horizontally, expanding the absorption area and preventing concentrated absorption of liquid, thereby improving the overall absorption efficiency of the sanitary pad.
Leak Guards: Some high-end sanitary napkins have additional leak guards, usually made from elastic materials, to prevent leakage.
Fragrances or Antibacterial Agents: Some products add fragrances or antibacterial agents to mask odors or reduce bacterial growth, but these may cause allergies or irritation in sensitive individuals.
Functional Chips: Such as negative ion chips, which can effectively inhibit bacterial growth and remove odors.
Packaging Materials: Used to protect the product and maintain its integrity during storage and transportation.
The choice of materials for sanitary napkins directly affects women's skin health, reproductive health, personal comfort, and environmental impact. Therefore, when selecting sanitary napkins, women should prioritize those made from high-quality, additive-free, and eco-friendly materials to ensure their health and comfort. If you are looking for a sanitary napkin raw material supplier, lonsun is a good choice.
IMARC Group. (2025). Global Sanitary Napkin Market Expected to Reach USD 38.0 Billion by 2033.